System类和Runtime类
System类和Runtime类
System类
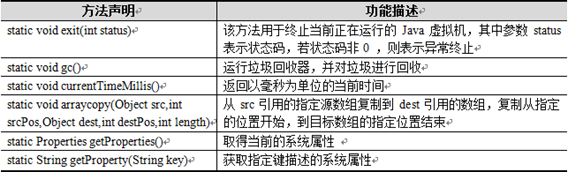
System类对读者来说并不陌生,因为在之前所学知识中,需要打印结果时,使用的都是“System.out.println();”语句,这句代码中就使用了System类。System类定义了一些与系统相关的属性和方法,它所提供的属性和方法都是静态的,因此,想要引用这些属性和方法,直接使用System类调用即可。System类的常用方法如下表所示。
1.getProperties()方法
System类的getProperties()方法用于获取当前系统的全部属性,该方法会返回一个Properties对象,其中封装了系统的所有属性,这些属性是以键值对形式存在的。
package cn.itcast.chapter05.example09;
import java.util.*;
/**
* System类的getProperties()方法
*/
public class Example09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前系统属性
Properties properties = System.getProperties();
// 获得所有系统属性的key,返回Enumeration对象
Enumeration propertyNames = properties.propertyNames();
while (propertyNames.hasMoreElements()) {
// 获取系统属性的键key
String key = (String) propertyNames.nextElement();
// 获得当前键key对应的值value
String value = System.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "--->" + value);
}
}
}
2.currentTimeMillis()
currentTimeMillis()方法返回一个long类型的值,该值表示当前时间与1970年1月1日0点0分0秒之间的时间差,单位是毫秒,通常也将该值称作时间戳。
package cn.itcast.chapter05.example10;
/**
* 计算程序在进行求和操作时所消耗的时间
*/
public class Example10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 循环开始时的当前时间
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) {
sum += i;
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 循环结束后的当前时间
System.out.println("程序运行的时间为:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
}
}
3.arraycopy(Object src,int srcPos,Object dest,int destPos,int length)
arraycopy()方法用于将一个数组中的元素快速拷贝到另一个数组。其中的参数具体作用如下:
- src:表示源数组。
- dest:表示目标数组。
- srcPos:表示源数组中拷贝元素的起始位置。
- destPos:表示拷贝到目标数组的起始位置。
- length:表示拷贝元素的个数。
package cn.itcast.chapter05.example11;
/**
* 数组元素的拷贝
*/
public class Example11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] fromArray = { 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106 }; // 源数组
int[] toArray = { 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207 }; // 目标数组
System.arraycopy(fromArray, 2, toArray, 3, 4); // 拷贝数组元素
// 打印目标数组中的元素
for (int i = 0; i < toArray.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + ": " + toArray[i]);
}
}
}
4.SystemClock.uptimeMillis()
Runtime类
Runtime类用于表示虚拟机运行时的状态,它用于封装JVM虚拟机进程。每次使用java命令启动虚拟机都对应一个Runtime实例,并且只有一个实例,因此该类采用单例模式进行设计,对象不可以直接实例化。若想在程序中获得一个Runtime实例,只能通过以下方式:

案例代码
由于Runtime类封装了虚拟机进程,因此,在程序中通常会通过该类的实例对象来获取当前虚拟机的相关信息。
package cn.itcast.chapter05.example12;
/**
* Runtime类的使用
*/
public class Example12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); // 获取
System.out.println("处理器的个数: " + rt.availableProcessors() + "个");
System.out.println("空闲内存数量: " + rt.freeMemory() / 1024 / 1024 + "M");
System.out.println("最大可用内存数量: " + rt.maxMemory() / 1024 / 1024 + "M");
}
}
案例代码
Runtime类中提供了一个exec()方法,该方法用于执行一个dos命令,从而实现和在命令行窗口中输入dos命令同样的效果。例如,通过运行“notepad.exe”命令打开一个Windows自带的记事本程序
package cn.itcast.chapter05.example13;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 使用exec()方法打开记事本
*/
public class Example13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); // 创建Runtime实例对象
rt.exec("notepad.exe"); // 调用exec()方法
}
}
打开记事本并在3秒后自动关闭
package cn.itcast.chapter05.example14;
/**
* 打开的记事本并在3秒后自动关闭
*/
public class Example14 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); // 创建一个Runtime实例对象
Process process = rt.exec("notepad.exe");// 得到表示进程的Process对象
Thread.sleep(3000); // 程序休眠3秒
process.destroy(); // 杀掉进程
}
}
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); // 获取CPU核心数
Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory(); // 获取应用被分配的最大内存